Faculty Development: The Resident in Difficulty
Courtney Humphrey, MD
The purpose of identifying a resident in difficulty is not for punishment, but rather for identification and remediation of deficiencies that can hinder professional development. A resident in difficulty may be identified as having academic problems, professional problems, or both.
Warning signs of a resident with academic difficulty may include defensiveness, unwillingness to precept patients, low in-service exam score, and minimal participation in rounds. Warning signs of a resident with professionalism problems may include hostility, conflicts with patients or staff, overconfidence, disorganization, tardiness, and unexcused absences. Choosing applicants wisely based on their United States Medical Licensing Examination (USMLE)/Comprehensive Osteopathic Medical Licensing Examination (COMLEX) scores, social interactions with current residents, interview skills, and interactions with the program coordinator are important steps in selecting residents who are likely to succeed. If the program has a behavioral health faculty member, he or she should also be involved in the interview process to pick up on subtle signs of professionalism problems.
Having a streamlined approach for identifying and remediating a resident in difficulty and having clear written standards can ease the process. Standards should be outlined for the program, for the year of training, and for each individual rotation. The evaluation system needs to be clearly defined, comprehensive, and tied to the outlined program standards. It should be designed and mapped to ACGME milestones and competencies.
For the past 5 months, our program has instituted the below sequence for managing residents in difficulty. This streamlined approach has allowed us to navigate the remediation process with the residents in an efficient manner.
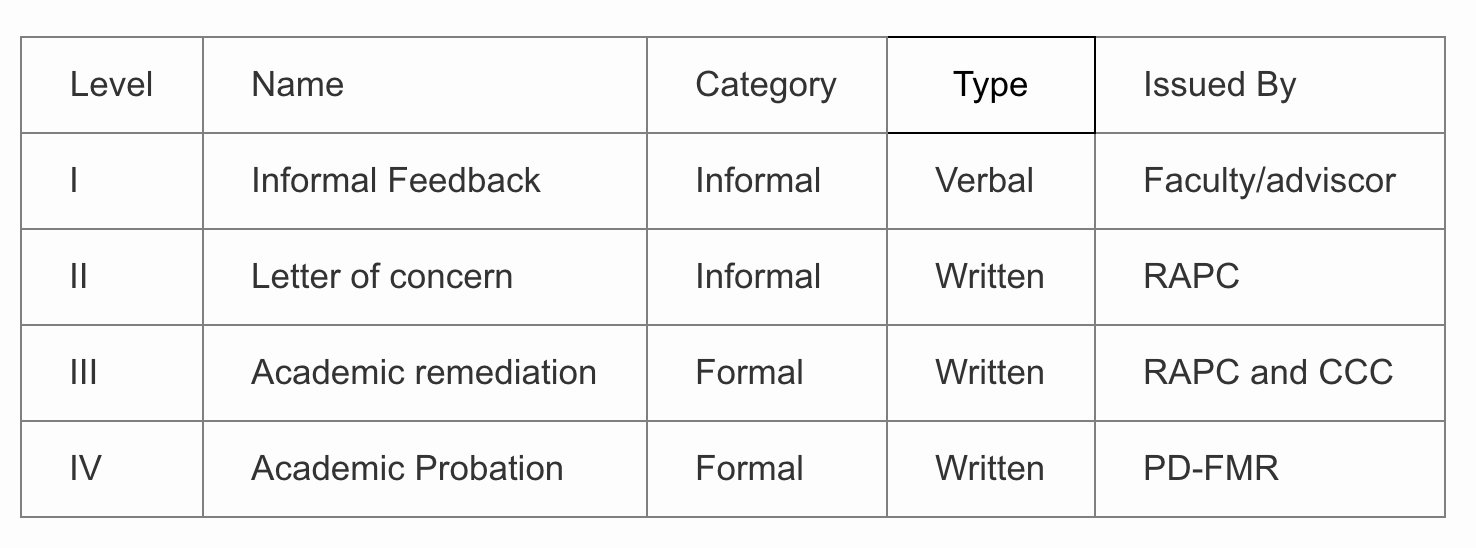
When a problem and or trend is observed, a discussion with the resident needs to ensue. This discussion should be held in private and be done by the resident’s faculty advisor. The issue should be described with details and specific examples. The tone of the conversation should be that of an open dialogue and nonaccusatory. Getting the resident’s viewpoint on the issue can help assess his or her understanding and insight. Referring the resident to the program’s Resident Academic and Professionalism Committee (RAPC) can help explore and address the issues related to the academic performance and/or professionalism behaviors using a balanced team approach. Appropriate documentation of the issues at hand by the program is important. A paper trail documenting the concerns and remedial action is critical for the program in the event that formal remediation or probation is warranted.
When a resident has been identified as “in difficulty,” it is important to intervene early and set expectations. Design an individualized learning plan (ILP) with the active input of the resident. Define expectations regarding the specific concern, including who will be involved, what will happen, and when the resident will be reevaluated. Addressing academic issues may include increased observation, independent study, procedural training courses, and supplemental testing. Addressing professionalism issues may include alternative schedules, counseling, referral to the employee assistance program, and approved leave of absence if indicated.
By outlining a clear path for the resident to follow to achieve success, the stress for both the faculty team and the resident is lessened.
